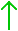
 BTC/USD
BTC/USD$ 98,125
 BTC/EUR
BTC/EUR€ 94,416
¥ 172,521 0%
 BTC/GBP
BTC/GBP£ 78,177
₽ 3,900,027 0%
$ 30.44B
$ 92.32B
$ 3.08T
Bitcoin is a digital currency invented or “proposed” by an unidentified software developer (or developers) known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It is a virtual peer-to- peer network that only exists electronically. Bitcoin is decentralized, it is not printed by a central authority (like a central bank in the case of fiat currency) but it is rather mined by a community of miners that anyone can join. It is part of a group of similar digital currencies called Cryptocurrencies (since they use encryption techniques to function) and it’s the largest in terms of total market capitalization. Bitcoin gained greater recognition in 2013 when its value broke the $1000 level.
| Bitcoin today’s price | |
| BTC/USD | $ 98124.46 |
| BTC/EUR | € 94415.25 |
| BTC/CNY | ¥ 172521.27 |
| BTC/GBP | £ 78176.92 |
| BTC/RUR | ₽ 3900027.00 |
Every transaction ever made in the Bitcoin network is recorded in the Blockchain, a global, distributed and public ledger; and all transactions need to be confirmed first by the community of miners. The process of mining serves two purposes: verifying the validity of transactions (in order to secure the system) and creating new Bitcoins each time a “block” of transactions is added to the Blockchain. Miners are rewarded with those newly created Bitcoins (and also transaction fees) for using their computational power to confirm and store transactions in the Blockchain. The first block of the Blockchain, called “the genesis block” was created on or after January 3, 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto.
Bitcoin is inherently deflationary because the system was mathematically designed to allow only 21 million Bitcoins to be mined and it is expected that the last Bitcoin will be generated near the year 2140; it was also designed to keep an average rate of only one block discovered each 10 minutes.
Bitcoin is decentralized, meaning it can’t be controlled by a single authority; it’s also distributed: even if a part of the network is shut down for some reason the Bitcoin network will continue to operate normally for the rest. Unless you permanently turn off the entire internet, you can’t destroy the Bitcoin network. Bitcoins cannot be counterfeited and the system protects against double spending; you cannot spend an amount of Bitcoins more than once.
Bitcoin is an open-source software, which means anyone can verify the code for themselves and the software can be developed in a collaborative public manner.
Unlike banks, Bitcoin offers anyone, anywhere the opportunity to create an address (or more) to store, send and receive Bitcoins instantly and for free, without any verification or long procedures.
Bitcoins can be sent directly between users and easily using the internet with minimal fees compared to other payment methods, as soon as the transaction is confirmed and is added to the Blockchain. A Bitcoin can be divided down to 8 decimal places which makes it easy to buy even at high prices.
Even though all transactions are recorded in the Blockchain, Bitcoin addresses do not contain any personal information that can be linked to the address holder.
For many, Bitcoin and the Blockchain technology will not only revolutionize the financial sector, but nearly every aspect of our daily lives.
Do you want Bitcoins? See our guide “How to buy Bitcoin”